The trick is to solve for one variable (such as y) in terms of the other variable (x) From the first equation, we know that y = 3x 15 Now, use the formula in the second equation 2x 3 (3x 15) = 17 That is, 7x 45 = 17 So, 7x = 28 or x = 28/7 = 4
Example 2 quad factorise x(x-y)^(3)+3x^(2y(x-y)- x^3 y^3 = (x y)(x^2 xy y^2) What is a perfect square binomial and how do you find the product? (iv) Let p(x) = 2y 3 y 2 2y 1 We shall find a factor of p(y) by using some trial value of y, say y = 1 p(1) = 2(1) 3 (1) 2 2(1) 1 = 2 1 2 1 = 0 Since the remainder of p(1) = 0, by factor theorem we can say y 1 is a factor of p(y) = 2y 3 y 2 2y 1 Now dividing p(y) by y 1 using long division, Therefore, 2y 3 y 2 2y 1 = (y 1) (2y 2 3y 1)
Example 2 quad factorise x(x-y)^(3)+3x^(2y(x-y)のギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
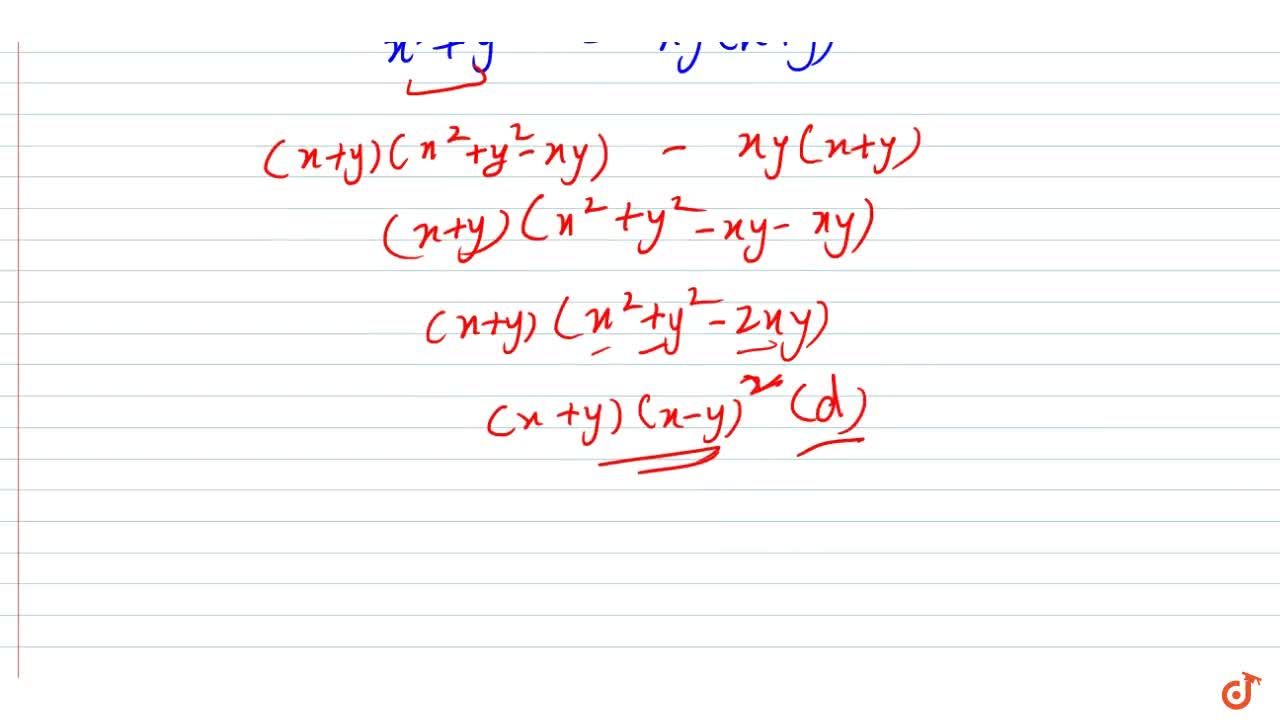 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 | ||
 |  |  |
「Example 2 quad factorise x(x-y)^(3)+3x^(2y(x-y)」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Example 2 quad factorise x(x-y)^(3)+3x^(2y(x-y)」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  | |
 |  | 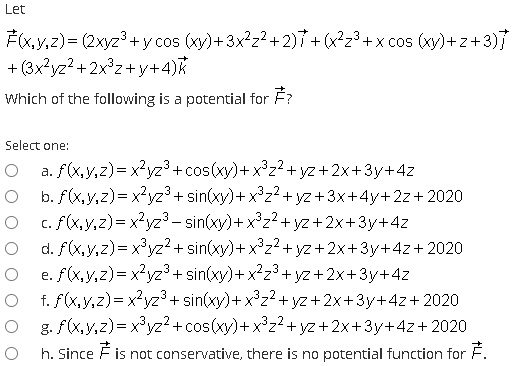 |
 |  | |
「Example 2 quad factorise x(x-y)^(3)+3x^(2y(x-y)」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「Example 2 quad factorise x(x-y)^(3)+3x^(2y(x-y)」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Example 2 quad factorise x(x-y)^(3)+3x^(2y(x-y)」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「Example 2 quad factorise x(x-y)^(3)+3x^(2y(x-y)」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 | ||
「Example 2 quad factorise x(x-y)^(3)+3x^(2y(x-y)」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 | ||
 |  | |
「Example 2 quad factorise x(x-y)^(3)+3x^(2y(x-y)」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | 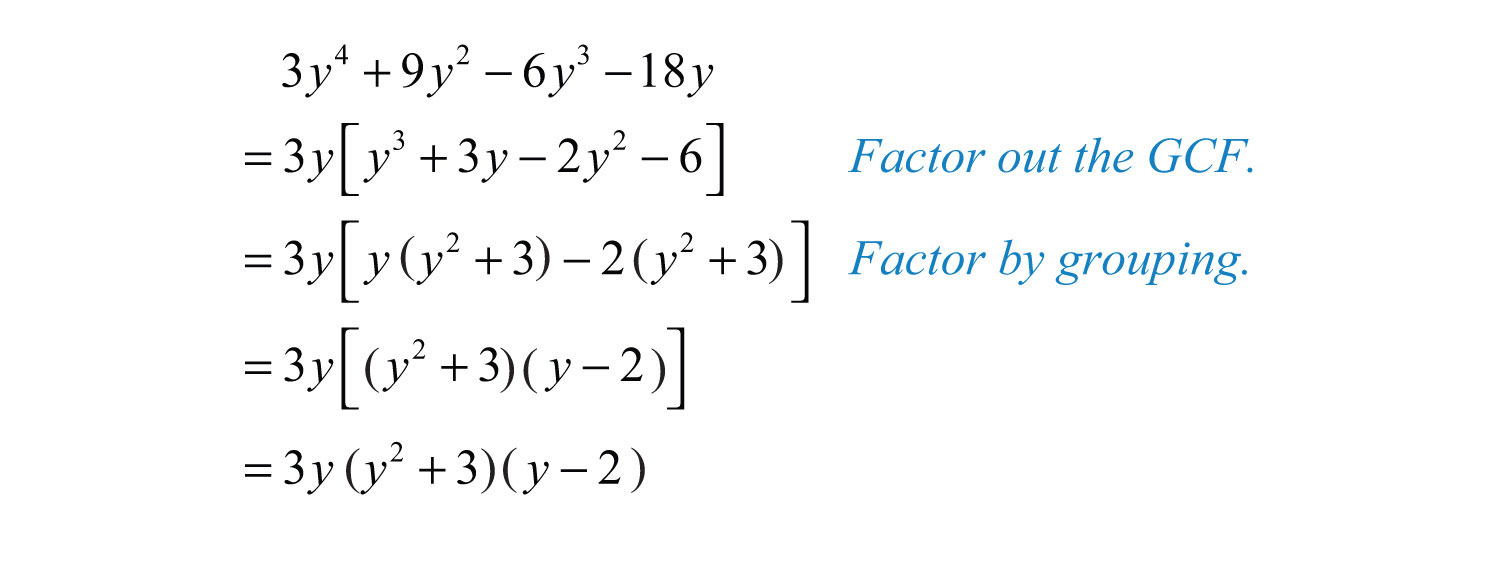 |
 |  | |
 |
Transcript Ex 24, 5 Factorise (i) x3 − 2x2 − x 2 Let p (x) = x3 – 2x2 – x 2 Checking p (x) = 0 So, at x = 1, p (x) = 0 Hence, x – 1 is a factor of p (x) Now, p (x) = (x – 1) g (x) ⇒ g (x) = (𝑝 (𝑥))/ ( (𝑥 − 1)) ∴ g (x) is obtained after dividing p (x) by xExample Factorize 9x 2 12xy 4y 2 Solution Step 1 Identify which identity can be applied in the expression We can apply (x y) 2 = x 2 2xy y 2 Step 2 Rearrange the expression so that it can appear in the form of the above identity 9x 2 12xy 4y 2 = (3x) 2 2 × 3x × 2y (2y) 2 Step 3 Once the expression is arranged in the form of the identity, write its factors
Incoming Term: x(x+y)^3-3x^2y(x+y) factorise, example 2 quad factorise x(x-y)^(3)+3x^(2y(x-y),




0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿